
Greenland’s Greening Crisis: Unveiling the Impact of Global Warming on the Arctic Landscape
- by dgihost.com
Greenland’s Dramatic Transformation: Global Warming Unleashes Surprising Changes
In a startling revelation, a recent study using satellite images has unveiled the profound impact of global warming on Greenland’s icy expanse. Titled “Greenland’s Greening Crisis,” the research found that over the past 30 years, approximately 11,000 square miles of Greenland’s once-frozen landscapes have succumbed to the effects of climate change.
The focus keyword for this article is “Greenland’s Greening Crisis,” shedding light on the unexpected consequences of rising temperatures in the Arctic region.
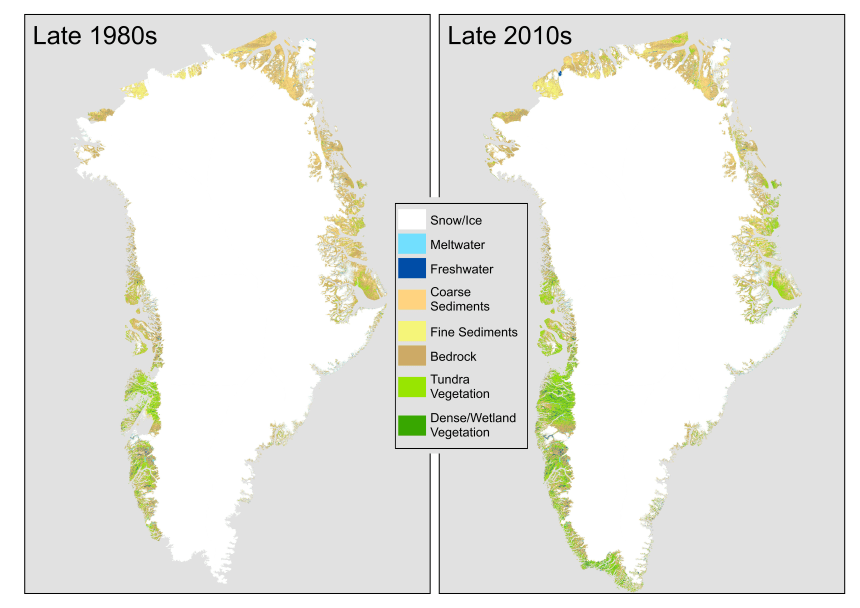
The study, published in the journal Scientific Reports, showcases how parts of Greenland’s ice sheet and glaciers, which melted during this period, have given way to wetlands, shrub vegetation, and barren rock. This transformation raises concerns about the stability of the landscape, heightened sea levels, and the release of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly in areas turning into methane-producing wetlands.
Greenland, often considered “ground zero” for the climate crisis, is susceptible to even minor temperature shifts, impacting the entire Arctic region and beyond. Scientists estimate that if the entire Greenland ice sheet were to melt, it could result in a staggering global sea-level rise of over 23 feet.
The study reveals that the affected area is approximately nine times the size of Rhode Island, equivalent to about 1.6% of Greenland’s total ice cover. Using satellite images, researchers observed a significant increase of 33,774 square miles in land with vegetation growth from the mid-1980s through the mid-2010s. Notably, the most substantial changes occurred in southwestern, eastern, and northeastern Greenland.
Wetlands, a key player in this transformation, nearly quadrupled across Greenland, particularly around the town of Kangerlussuaq on the western coast. The loss of ice triggers a chain reaction, leading to further ‘greening,’ where exposed rock becomes colonized by tundra and eventually shrub.
Jonathan Carrivick, an Earth scientist at the University of Leeds and one of the study’s authors, warns, “We have seen signs that the loss of ice is triggering other reactions which will result in further loss of ice and further ‘greening’ of Greenland.”
The consequences extend beyond the visible changes, affecting the overall temperature of the land. As ice retreats, the exposed bedrock and new vegetation absorb more of the sun’s energy, exacerbating global warming.
The article’s focus keyword, “Greenland’s Greening Crisis,” emphasizes the urgency and severity of the situation. Wetlands, formed as a result, house microbes releasing methane, a potent greenhouse gas, becoming significant emission sources.
Michael Grimes, the lead author of the study, notes the cultural impact on indigenous populations, relying on these ecosystems for traditional practices. Moreover, the loss of ice in Greenland significantly contributes to global sea-level rise, posing challenges now and in the future.
In conclusion, the transformation of Greenland’s landscape highlights the critical need for urgent climate action. “Greenland’s Greening Crisis” underscores the far-reaching consequences of global warming, urging a collective effort to mitigate environmental degradation and preserve our planet for future generations.
Greenland’s Dramatic Transformation: Global Warming Unleashes Surprising Changes In a startling revelation, a recent study using satellite images has unveiled the profound impact of global warming on Greenland’s icy expanse. Titled “Greenland’s Greening Crisis,” the research found that over the past 30 years, approximately 11,000 square miles of Greenland’s once-frozen landscapes have succumbed to the…